Guide to CIPC ESG Reporting Preparation in 2024
ESG has emerged as a pressing global concern, with both jurisdictions and companies facing growing pressure to transparently report their environmental, social, and governance impacts within their communities. This issue also holds significant national importance, as the government seeks to ensure corporate accountability in reporting while fostering a proactive culture of transparency.
The CIPC is actively involved in overseeing compliance with IFRS standards. With the launch of new IFRS standards for sustainability reporting, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) aims to begin preparations for integrating the ESG taxonomy into CIPC’s existing base National Green Finance taxonomy. This update will include ESG taxonomy elements, providing a valuable resource for various reporting entities.
With the integration of ESG standards into the taxonomy, South African companies are advised to prepare and file ESG reports with CIPC in the fourth fiscal quarter (Q4) 2023.
IFRS S1 – Sustainability Related Financial Disclosure Information
IFRS S2 – Climate Related Disclosure Standards
Navigating the Evolving ESG Reporting Landscape in South Africa
South Africa has been taking significant strides to align its reporting framework with global sustainability initiatives. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) recently engaged with major African economies to promote sustainability standards, highlighting the importance of accurate data to these mandates in South Africa.
Understanding the ESG Reporting Framework
In recent years, South Africa has experienced a significant shift in the ESG reporting landscape, catalyzed by increasing demands for transparent and comprehensive disclosures. Central to this evolution is the development of the ESG reporting framework, spearheaded by entities such as the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE).
ESG reporting framework serves as a guiding structure for companies to assess and report on their environmental, social, and governance performance. By understanding the nuances of this framework, businesses can effectively align their reporting practices with regulatory expectations and stakeholder demands.
Introducing a New ESG Framework for South Africa
The Companies and Intellectual Property Commission (CIPC) has embarked on a significant initiative by introducing mandatory Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting alongside XBRL filing. Initially voluntary starting from Q4 of 2023, this framework will transition to mandatory status from 2025 onwards, with a focus on public and state-owned enterprises and more detailed tagging requirements. This robust reporting framework aims to elevate transparency and accountability, providing vital support for internal decision-making processes and bolstering external stakeholder confidence.
Exploring the Pillars of ESG
ESG reporting revolves around three core pillars, each crucial for assessing a company’s impact and responsibility:
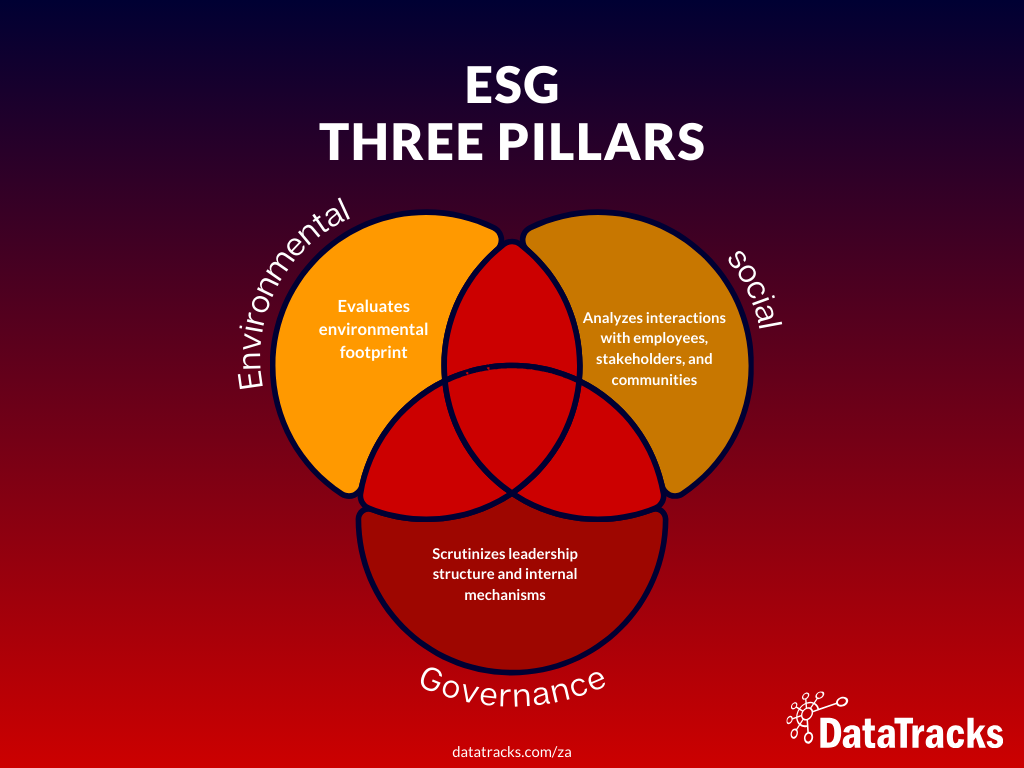
Environmental
This dimension evaluates a company’s environmental footprint, covering aspects such as energy consumption, waste management practices, pollution control measures, and initiatives aimed at addressing climate change.
Social
This pillar delves into a company’s interactions with its employees, stakeholders, and the broader community. It encompasses areas such as labour practices, diversity and inclusion initiatives, adherence to health and safety standards, and the level of engagement with local communities.
Governance
This component scrutinizes a company’s leadership structure and internal mechanisms, including board composition, executive compensation policies, the effectiveness of risk management practices, and the commitment to ethical business conduct.
By embracing and effectively implementing this holistic ESG framework, companies can not only showcase their dedication to sustainable practices but also strengthen their resilience and competitiveness in South Africa’s dynamic business environment.
Integrating the Green Finance Taxonomy into ESG Reporting
Understanding the Objectives
South Africa’s introduction of the Green Finance Taxonomy marks a significant step towards sustainable finance. Developed over two years by the Taxonomy Working Group, it provides clear guidelines for identifying green investments that align with international best practices and national priorities.
Green Finance Taxonomy offers numerous advantages within the ESG reporting framework
- Clarity and Certainty: It provides clear guidelines for selecting green investments, enhancing decision-making processes.
- Risk Reduction: Emphasizing environmental and social performance helps mitigate financial risks associated with unsustainable practices.
- Cost Efficiency: Streamlined labeling and issuance processes lower costs for green financial instruments.
- Investment Opportunities: Unlocking a broad range of green assets fosters investment in climate-friendly projects.
- Regulatory Support: The Taxonomy aids regulatory oversight and provides a basis for aligning or referencing green financial products.
Integrating the Green Finance Taxonomy into ESG reporting facilitates sustainable investments, fosters accountability, and advances South Africa’s climate goals in line with global efforts.
Need for ESG Reporting in South Africa
Several countries around the globe, like the EU and the US, have already implemented ESG reporting due to its benefits for different stakeholders. Considering these advantages, the CIPC board has initiated ESG reporting in Q4 for South Africa.
ESG reporting benefits the government, businesses, and consumers in the following ways:
- Governments worldwide are making stricter rules for reporting to ensure companies are open and transparent about their sustainability practices.
- Businesses recognize the benefits of disclosing ESG data to attract investors and customers seeking responsible and sustainable investments.
- Consumers are also becoming more aware of the impact of their purchasing decisions on society and the environment. As a result, they are demanding more accountability from companies.
Embracing ESG Standards for Enhanced Transparency and Accountability
As South Africa moves towards a more standardized approach to ESG reporting, embracing established ESG standards becomes imperative. These standards, set forth by organizations like the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), provide a common language and framework for reporting ESG performance.
By adhering to these standards, companies can enhance transparency, comparability, and credibility in their ESG disclosures. Moreover, embracing ESG standards demonstrates a commitment to accountability and responsible corporate citizenship, earning the trust and confidence of investors, regulators, and other stakeholders.
Who Should File ESG Reports to CIPC?
CIPC implemented XBRL filing in South Africa in July 2018. After five years of mandate, the regulatory body is introducing ESG reporting in Q4 of 2023 alongside XBRL filing. Significant developments have shaped South Africa’s ESG reporting scene in recent years, primarily driven by a growing need for transparent and accurate disclosure of ESG aspects.
South African companies that are required to file ESG reports to CIPC in iXBRL format include:
- Public companies
- State-owned companies
The companies mentioned above can opt for voluntary filing in Q4 2023. From next year, companies will be mandated to disclose their ESG information with minimum tagging. From the financial year 2025-26, the disclosure will be mandated with moderate and detailed tagging.
Preparing for ESG Reporting in South Africa
How Can South African Companies Get Ready for ESG Regulations?
In South Africa, there are rules, like the ESG reporting requirements from the Johannesburg Stock Exchange and the Green Finance Taxonomy, that make companies share their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks and opportunities. By collecting and sharing data accurately, South African companies can meet these rules and also make their reputation stronger and stay competitive. Accurate reporting isn’t just about following the rules; it also helps investors and stakeholders see how a company is working to be sustainable, so they can make better decisions and hold companies accountable.
To keep up with these rules and make sure they’re following them, companies need to pay attention to sustainability issues and changes in the rules. By staying informed about what’s going on with sustainability rules and regulations, companies can take steps to prevent environmental and social problems, find chances to grow sustainably, and meet new rules as they come up. Taking these steps helps South African companies move forward while making the world a better place.
DataTracks: CIPC’s Approved Software and Service Provider for ESG Reporting!
In the coming years, CIPC may develop its own taxonomy for ESG reporting. However, since ESG reporting began in South Africa, CIPC has adopted the European Union’s taxonomy for sustainability disclosures. What is the best in business for ESG reporting in the EU? DataTracks!
While ESG reporting may be new to your business, it is not for DataTracks! The experts at DataTracks have experience preparing ESG reports for several other regions like the EU, UK, and US. The company has robust software, making it well-equipped to prepare ESG reports. All you need to do is provide your financial reports, and the DataTracks professionals will prepare error-free iXBRL and ESG reports. So if you want a smooth transition into ESG reporting in the coming quarter, outsource your requirements to DataTracks! Contact an expert @ +27-10-446-9061 or e-mail enquiry@datatracks.co.za.
FAQs on ESG Reporting Landscape in South Africa
What is the significance of the ESG reporting framework in South Africa?
The ESG reporting framework plays a pivotal role in South Africa’s business landscape, aligning with global sustainability initiatives and emphasizing the importance of considering societal and environmental impacts alongside financial metrics.
How do South African companies comply with ESG reporting requirements?
South African companies adhere to ESG reporting mandates set by regulatory frameworks such as the Johannesburg Stock Exchange and the Green Finance Taxonomy. Compliance involves accurately collecting and reporting data to meet regulatory demands and enhance reputation and competitiveness.
What are the key benefits of accurate ESG reporting for South African companies?
Accurate ESG reporting not only satisfies regulatory requirements but also provides valuable insights into a company’s sustainability efforts, fostering informed decision-making and accountability for ESG performance. It also enhances reputation and competitiveness in the market.
How can South African companies stay ahead of evolving ESG regulations?
To remain compliant with evolving regulations, companies must proactively engage with sustainability issues and developments. Staying informed about sustainability frameworks and regulations empowers companies to address risks preemptively, seize growth opportunities, and align with emerging regulatory expectations.
Who is required to file ESG reports to the CIPC in South Africa?
Public and state-owned companies in South Africa are mandated to file ESG reports alongside XBRL filings to the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission (CIPC). Initially voluntary, these reports transition to mandatory disclosure starting from the financial year 2025-26. The CIPC’s initiative, starting as voluntary in Q4 2023 and becoming compulsory from 2025 onwards, aims to enhance transparency and accountability. Focused on public and state-owned enterprises, this framework supports internal decision-making and increases external stakeholder confidence, underscoring the significance of sustainability in South Africa’s business landscape.




