Comprehensive Guide to XBRL Filing Due Dates, Penalties and Fees for FY 2023-24
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial compliance, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in India mandates various filing requirements to ensure transparency and adherence to regulatory standards. One critical aspect of this compliance is XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) filing, which enables standardized digital reporting of financial information. This blog will provide an in-depth look at the due dates for XBRL filing with the MCA, helping businesses stay compliant and avoid penalties.
What is XBRL Filing?
XBRL is a global standard for exchanging and reporting business information. It facilitates the electronic communication of financial data, allowing for accurate, efficient, and standardized reporting. The MCA has adopted XBRL to streamline the submission of financial statements, ensuring consistency and clarity in financial reporting across companies.
Key Due Dates for Compliance Filing with the MCA
- Annual Financial Statements (AFS):
- Due Date: 30 days from the date of the Annual General Meeting (AGM).
- Details: Companies are required to file their annual financial statements, including balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, and other financial reports, in XBRL format. This ensures that financial statements are easily accessible and comparable across different entities.
- Annual Return:
- Due Date: 60 days from the date of the AGM.
- Details: Alongside financial statements, companies must file their annual return, which includes details about shareholders, directors, and other key corporate data. The XBRL format helps in maintaining a comprehensive and up-to-date record of the company’s status.
- Quarterly Financial Statements:
- Due Date: 45 days from the end of each quarter.
- Details: For listed companies, quarterly financial statements need to be filed within 45 days from the end of each quarter. This periodic reporting is crucial for investors and stakeholders to monitor the company’s performance.
- Compliance Report for Listed Companies:
- Due Date: 60 days from the end of each financial year.
- Details: Listed companies must submit a compliance report that outlines adherence to various regulatory requirements. This report should be filed in XBRL format to ensure uniformity and transparency.
- Form 23AC (for filing financial statements):
- Due Date: Within 30 days of the AGM.
- Details: This form is used for filing financial statements under Section 220 of the Companies Act. It must be submitted along with the XBRL version of the financial statements.
- Form 66 (Compliance Certificate):
- Due Date: Within 30 days from the end of the financial year.
- Details: Companies must file Form 66, which certifies compliance with various statutory requirements. The XBRL format ensures that this certification is consistent with the reported financial data.
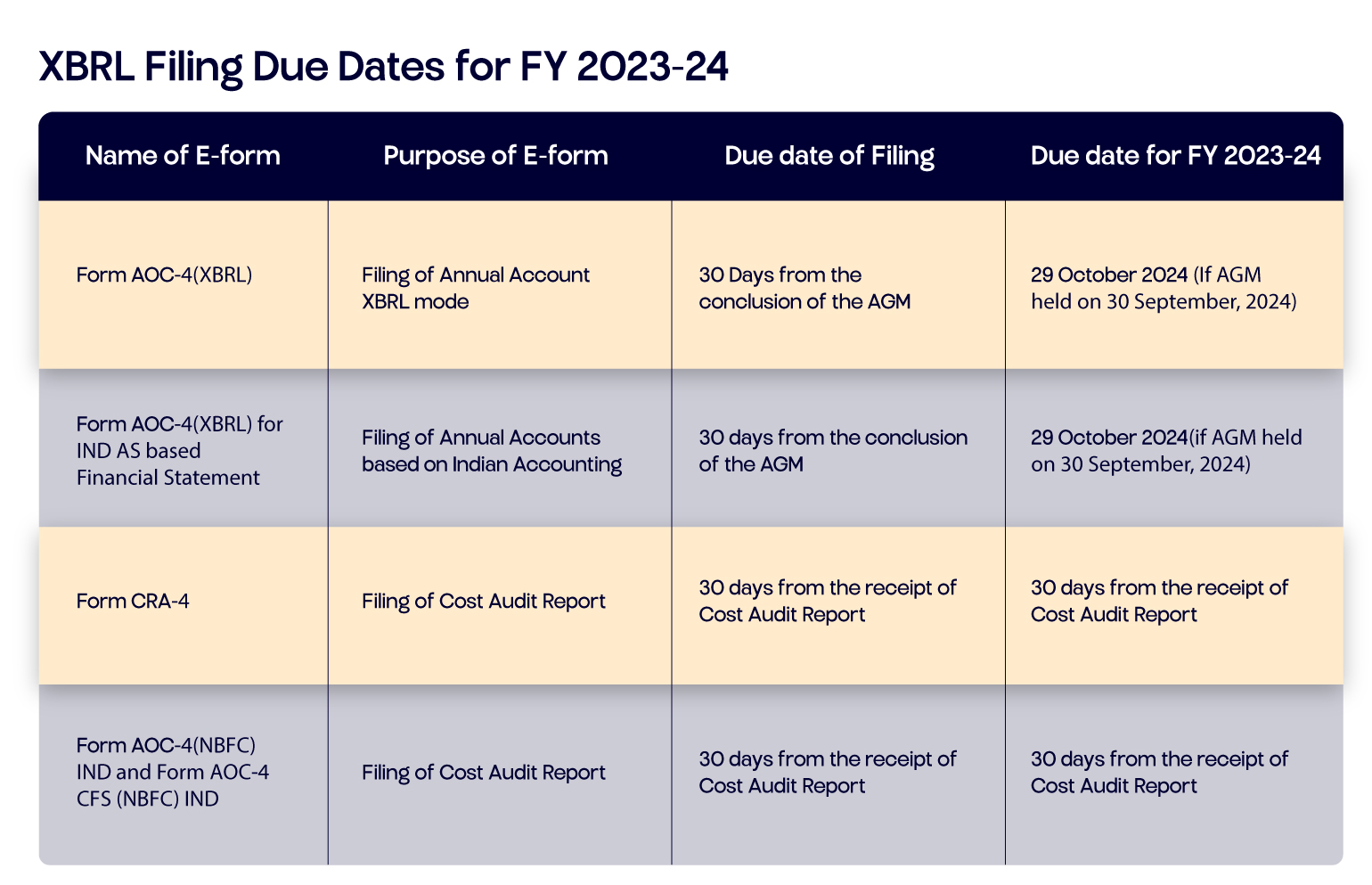
XBRL Filing Due Dates for FY 2023-24: A Comprehensive Guide
For the financial year 2023-24, the following are the critical due dates for various e-forms related to XBRL filings:
1. Form AOC-4 Due Date (XBRL)
- Purpose: Filing of Annual Accounts in XBRL mode.
- Due Date: 30 days from the conclusion of the Annual General Meeting (AGM).
- Due Date for FY 2023-24: October 29, 2024 (if AGM is held on September 30, 2024).
2. Form AOC-4 (XBRL) for IND AS Based Financial Statements
- Purpose: Filing of Annual Accounts based on Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS) in XBRL mode.
- Due Date: 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM.
- Due Date for FY 2023-24: October 29, 2024 (if AGM is held on September 30, 2024).
3. Form CRA-4
- Purpose: Filing of Cost Audit Report.
- Due Date: 30 days from the receipt of the Cost Audit Report.
- Due Date for FY 2023-24: 30 days from the receipt of the Cost Audit Report (exact date will depend on when the report is received).
4. Form AOC-4 (NBFC) IND and Form AOC-4 CFS (NBFC) IND
- Purpose: Filing of Annual Accounts based on Indian Accounting Standards for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- Due Date: 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM.
- Due Date for FY 2023-24: 30 days from the conclusion of the AGM.
Understanding Penalties and Additional Fees for Late XBRL Filings
Timely filing of XBRL forms with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) is crucial to avoid additional costs and penalties. This guide outlines the penalty structure for late filings, helping companies understand the financial implications of delayed submissions.
Additional Fees for Late Filing
E-Form AOC-4 (XBRL and Non-XBRL) and Form MGT-7
- Additional Fee: INR 100 per day, effective from July 1, 2018.
- Application: This fee applies to late submissions of E-Form AOC-4 (both XBRL and Non-XBRL) and Form MGT-7.
Penalty Structure for Other Forms and Documents
The penalty for late submission of other forms and documents varies depending on the duration of the delay:
- Up to 30 Days:
- Fee: 2 times the normal fee.
- Details: A moderate penalty for short delays. Companies should aim to file within this period to minimize additional costs.
- More than 30 Days and Up to 60 Days:
- Fee: 4 times the normal fee.
- Details: The penalty increases significantly, reflecting the extended delay. Companies should prioritize filing within this window to avoid higher costs.
- More than 60 Days and Up to 90 Days:
- Fee: 6 times the normal fee.
- Details: This period incurs a substantial penalty, indicating the need for prompt action to avoid escalating fees.
- More than 90 Days and Up to 180 Days:
- Fee: 10 times the normal fee.
- Details: A severe penalty is imposed for delays extending up to 180 days. Companies face considerable additional costs if filing is not completed promptly.
- More than 180 Days and Up to 270 Days:
- Fee: 12 times the normal fee.
- Details: The maximum penalty for significant delays. Companies should avoid reaching this stage to prevent extremely high fees.
Key Takeaways
- Accuracy and Timeliness: Ensure that all filings are accurate and submitted on time to avoid penalties and maintain compliance.
- Documentation: Prepare and review all necessary documents and reports well in advance of the due dates.
- Consult Professionals: Engage with financial and compliance experts to assist with preparing and submitting XBRL filings.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of XBRL filing with the MCA can be challenging, but understanding the due dates and requirements is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance. By adhering to the prescribed deadlines and leveraging technology, companies can ensure their financial reporting is accurate, transparent, and timely.
For further assistance or to stay updated on regulatory changes, consult with XBRL experts or visit the official MCA website.
Reference:
XBRL Filing Due Dates



